Option Trading Strategies? Sounds difficult? Already worried? Well, don’t worry! We’ll help you break this down easily.
Here, we will discuss the Options Strangle Strategy (Short Strangle vs Long Strangle)
Options Trading Strategies
Option trading strategies use simple, “one-legged” orders to complex “multi-legged” orders. But simple or complex, what all strategies have in common is that they are based on two fundamental option types: CALL and PUT.
Strangle
Strangle is an options strategy where you can buy (or sell) a CALL and PUT with the same expiry date but with a different strike price.
Let us understand these strategies one by one.
-
-
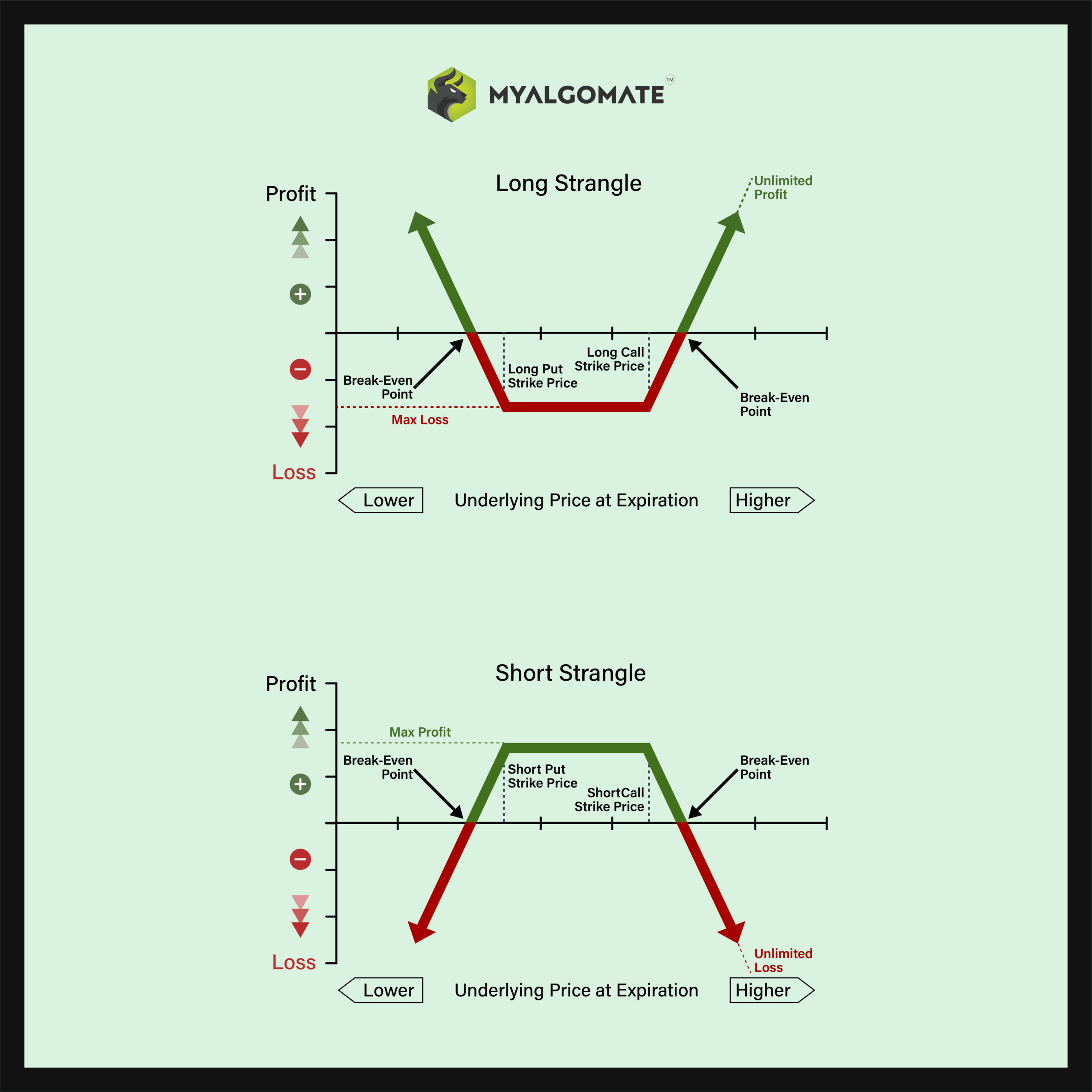
Short Strangle (Sell Strangle)
-
Long Strangle (Buy Strangle)
-
Also, check Options Straddle Strategy (Short Straddle vs Long Straddle)
The automated version of this strategy is readily available at Myalgomate Marketplace as Time Based Options Straddle/Options Strangle.
Short Strangle (Sell Strangle) Options Trading Strategy
| Strategy Level | Advance |
| Instruments Traded | Call + Put |
| Number of Positions | 2 |
| Market View | Neutral |
| Risk Profile | Unlimited |
| Reward Profile | Limited |
| Breakeven Point | 2 Breakeven points |
The Short Strangle (or Sell Strangle) is a neutral strategy wherein a Slightly OTM Call and a Slightly OTM Put Options are sold simultaneously of the same underlying asset and expiry date.
This strategy can be used when the trader expects that the underlying stock will experience very little volatility in the near term.
It is a limited profit and unlimited risk strategy. The maximum profit earn is the net premium received. The maximum loss is achieved when the underlying moves either significantly upwards or downwards at expiration.
A net credit is taken to enter into this strategy. For this reason, the Short Strangles are Credit Spreads.
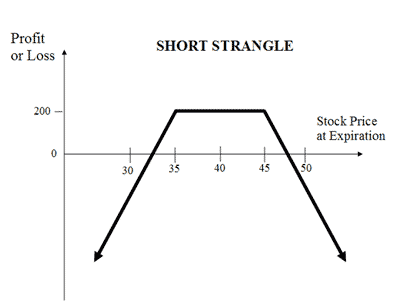
The usual Short Strangle Strategy looks like as below for NIFTY current index value at 18000 (NIFTY Spot Price):
| Orders | NIFTY Strike Price |
|---|---|
| Sell 1 Slightly OTM Put | NIFTY18APR17800PE |
| Sell 1 Slightly OTM Call | NIFTY18APR18200CE |
Suppose Nifty is currently at 18000 and you expect not much movement in near future. In such a scenario, you can execute a short strangle strategy by selling Nifty Put and Call at 17800 and 18200. The net premium received will be your maximum profit while the loss will depend on how high or low the index moves.
What about Theta (Time) Decay?
Theta decay for a short strangle is highly beneficial.
Regardless of the direction the underlying asset moves, time premium will come out of the short options. For every trading day that passes until expiration, sellers of the call and put options in a short strangle will collect time premium.
Important Tips for Selling Strangles
Short strangles seem to combine the best of both worlds when selling options. If the underlying asset moves up slightly, moves down slightly, or stays the same, traders will make money.
Something to watch out for with short strangles is sharp increases in volatility or huge, unexpected moves in the price of the underlying. Usually, these two events go hand in hand. If either event occurs, the losses for the short strangle options strategy can be severe.
Long Strangle (Buy Strangle) Options Trading Strategy
| Strategy Level | Beginners |
| Instruments Traded | Call + Put |
| Number of Positions | 2 |
| Market View | Neutral |
| Risk Profile | Limited |
| Reward Profile | Unlimited |
| Breakeven Point | 2 Breakeven points |
The Long Strangle (or Buy Strangle or Option Strangle) is a neutral strategy wherein Slightly OTM Put Options and Slightly OTM Call are bought simultaneously with the same underlying asset and expiry date.
This strategy can be used when the trader expects that the underlying stock will experience significant volatility in the near term.
It is a limited risk and unlimited reward strategy. The maximum loss is the net premium paid while maximum profit is achieved when the underlying moves either significantly upwards or downwards at expiration.
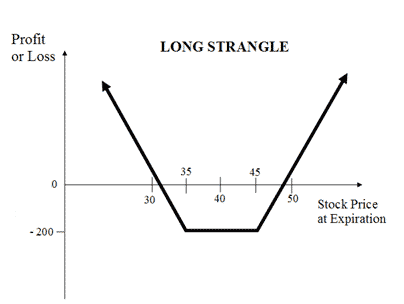
The usual Long Strangle Strategy looks like as below for NIFTY current index value at 18000 (NIFTY Spot Price):
| Orders | NIFTY Strike Price |
|---|---|
| Buy 1 Slightly OTM Put | NIFTY18APR17800PE |
| Buy 1 Slightly OTM Call | NIFTY18APR18200CE |
Suppose Nifty is currently at 18000 and due to some upcoming events you expect the price to move sharply but are unsure about the direction. In such a scenario, you can execute a long strangle strategy by buying Nifty Put at 17800 and buying Nifty Call at 18200. The net premium paid will be your maximum loss while the profit will depend on how high or low the index moves.
What about Theta (Time) Decay?
Theta decay is very detrimental to a long strangle because there are two long options positions. As expiration approaches, the long call and long put components of a long strangle are going to decrease in value solely due to time premium decay. Timing is critical for making money with long strangles.
Important Tips for Buying Strangles
For the most part, traders use the long strangle option strategy when they anticipate large movements in an underlying asset, but they just don’t know whether the movements will be up or down. The long strangle is a popular strategy to deploy on individual stocks, often before earnings reports. Individual stocks seem to have more upside and downside risk than other assets, like indices.
Not only will a long strangle benefit from significant up or down moves in the underlying, but it will also benefit from spikes in volatility. This is very important to be aware of upon order entry. Calls and puts become more expensive when volatility increases.
Because a long strangle doesn’t involve any short options positions, the risk is limited and very conservative relative to the maximum potential profit. As far as trading options go, strangles are one of the most conservative strategies due to the defined risk.
Comparison: Long Strangle (Buy Strangle) Vs Short Strangle (Sell Strangle)
| Long Strangle (Buy Strangle) | Short Strangle (Sell Strangle) | |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
|
| About Strategy | The Long Strangle (or Buy Strangle or Option Strangle) is a neutral strategy wherein Slightly OTM Put Options and Slightly OTM Call are bought simultaneously with the same underlying asset and expiry date. This strategy can be used when the trader expects that the underlying stock will experience significant volatility in the near term. | The Short Strangle (or Sell Strangle) is a neutral strategy wherein a Slightly OTM Call and a Slightly OTM Put Options are sold simultaneously of the same underlying asset and expiry date. This strategy can be used when the trader expects that the underlying stock will experience very little volatility in the near term. |
| Market View | Neutral | Neutral |
| Strategy Level | Beginners | Advance |
| Options Type | Call + Put | Call + Put |
| Number of Positions | 2 | 2 |
| Risk Profile | Limited | Unlimited |
| Reward Profile | Unlimited | Limited |
| Breakeven Point | 2 Breakeven points | 2 Breakeven points |
When and how to use Long Strangle (Buy Strangle) and Short Strangle (Sell Strangle)?
| Long Strangle (Buy Strangle) | Short Strangle (Sell Strangle) | |
|---|---|---|
| When to use it? | A Long Strangle is meant for special scenarios where you foresee a lot of volatility in the market due to election results, budget, policy change, annual result announcements, etc. | The Short Strangle is perfect in a neutral market scenario when the underlying is expected to be less volatile. |
| Market View | Neutral
When you are unsure of the direction of the underlying but expecting high volatility in it. |
Neutral
When you are expecting little volatility and movement in the price of the underlying. |
| Action |
Suppose Nifty is currently at 10400 and you expect the price to move sharply but are unsure about the direction. In such a scenario, you can execute a long strangle strategy by buying Nifty at 10600 and 10800. The net premium paid will be your maximum loss while the profit will depend on how high or low the index moves. |
Sell 1 out-of-the-money put and sell 1 out-of-the-money call which belongs to the same underlying asset and has the same expiry date. |
| Breakeven Point | two break-even points
An Options Strangle strategy has two break-even points. Lower Breakeven Point = Strike Price of Put – Net Premium Upper Breakeven Point = Strike Price of Call + Net Premium |
two break-even points
A strangle has two break-even points. Lower Break-even = Strike Price of Put – Net Premium Upper Break-even = Strike Price of Call+ Net Premium” |
Compare Risks and Rewards (Long Strangle (Buy Strangle) Vs Short Strangle (Sell Strangle))
| Long Strangle (Buy Strangle) | Short Strangle (Sell Strangle) | |
|---|---|---|
| Risks | Limited
Max Loss = Net Premium Paid The maximum loss is limited to the net premium paid in the long strangle strategy. It occurs when the price of the underlying is trading between the strike price of Options. |
Unlimited
The maximum loss is unlimited in this strategy. You will incur losses when the price of the underlying moves significantly either upwards or downwards at expiration. Loss = Price of Underlying – Strike Price of Short Call-Net Premium Received Or Loss = Strike Price of Short Put – Price of Underlying – Net Premium Received |
| Rewards | Unlimited
Maximum profit is achieved when the underlying moves significantly up and down at expiration. Profit = Price of Underlying – Strike Price of Long Call-Net Premium Paid Or Profit = Strike Price of Long Put – Price of Underlying – Net Premium Paid |
Limited
For maximum profit, the price of the underlying expiration date must trade between the strike prices of the options. The maximum profit is limited to the net premium received while selling the Options. Maximum Profit = Net Premium Received |
| Maximum Profit Scenario | One Option exercised | Both Options not exercised |
| Maximum Loss Scenario | Both Options not exercised | One Option exercised |
Pros & Cons of Long Strangle (Buy Strangle) and Short Strangle (Sell Strangle)
| Long Strangle (Buy Strangle) | Short Strangle (Sell Strangle) | |
|---|---|---|
| Advantages | The strategy offers a higher chance of profitability in comparison to Short Straddle due to the selling of OTM Options. | |
| Disadvantage | The strategy requires significant price movements in the underlying to gain profits. | Limited reward with high-risk exposure. |
| Similar Strategies | Long Straddle, Short Strangle | Short Straddle, Long Strangle |
What’s Next?
I hope you enjoyed reading about algorithmic trading strategies.
check out our next blog on Detailed information on Options Straddle Strategy (Short Straddle vs Long Straddle)
Disclaimer: All data and information provided in this article are for informational purposes only. Myalgomate™ makes no representations as to accuracy, completeness, correctness, suitability, or validity of any information in this article and will not be liable for any errors, omissions, or delays in this information or any losses, injuries, or damages arising from its display or use. All information is provided on an as-is basis.


1 Comment
Options Straddle Strategy (Short Straddle Vs Long Straddle) - Myalgomate
November 11, 2021[…] Also, check Options Strangle Strategy (Short Strangle vs Long Strangle) […]