What is Algorithmic Trading?
Algorithmic trading simply means a process that helps to make trading orders automatically. It is more profitable than manual trading because it offers so much trading profit. All because it is faster and more accurate!
According to a report “Global Algorithmic Trading Market 2018-2022” by Research and Markets, iif you have to believe the data, the size of the algorithmic trading market is expected to grow from $ 11.1 billion in 2019 to $ 18.8 billion by 2024, growth in CAGR of 11.1 percent. In addition, it is widely used and expands its frequent access to emerging markets.
Here, this article is aimed to give you a thorough understanding of the following:
- What and Why of Algorithmic Trading?
- The Transformation from Manual to Algo Trading
- When did Algorithmic Trading start?
- Frequencies of Trading: HFT, MFT, LFT
- Algo Trading Strategies
- What are the Rules and Regulations in India?
- How to Learn Algorithmic Trading
- The workflow of Algorithmic Trading
What and Why of Algorithmic Trading?
In simple terms, Algorithmic Trading is the process of transforming a trading strategy into a computer code that buys and sells (sets) trading stocks in an automated, fast, and accurate way. As the Automated trading method is faster and more accurate, it is popular these days and expands its reach to emerging markets rapidly.
Technically, there are a number of statistical systems used to make trading decisions on the basis of current market data, sending and placing orders in the financial markets. This approach makes trading less of an individual’s emotional impact (such as fear, greed, etc.) because decisions to make each trade are computerized in an orderly fashion.
For example, the algorithm buys Apple shares (AAPL) if the current market share price is below the standard 200-day value. On the other hand, it would sell Apple shares (AAPL) if the current market price exceeds the average value of 200 days.
Okay, let’s move on and understand in general, how trading started and its transformation from a manual to an algorithm.
The transformation from Manual to Algorithmic Trading?
Now, you have a good idea of what algorithmic trading is and how it has gained a higher hand than conventional/manual trading. But how did they trade in the past when automation was non-existent.
Trading in the past and trading now!
Conventional trading was pre-algorithmic trading. In the past, people used to trade by hand by setting up telephone and computer trading.
Back in time, when the concept of automated trading was not introduced, traders would gather information from the market, analyze it, and make trading decisions accordingly.
So, historically, there have been human traders who could make decisions to buy or sell stocks based on market data.
Over time, the need for speed, reliability (without human emotions), and precise approach led to the development of algorithmic trading.
You can read about the benefits of algorithmic trading here. And now, let’s move on to understanding what happened after the advent of Algorithmic trading.
Does Algo trading affect traditional traders?
When you talk about algorithmic trading over traditional trading, it is clear that trading algorithms are very fast and accurate without human error.
According to the findings of the Economic Times in 2019, algorithm trading is the future of financial markets and a necessity for doing well in futures markets. Besides, algorithmic trading is considered harmless to traditional traders. This is because human intervention will always be needed to improve markets and ensure financial market stability.
Now that you know what trading was like before automation took over, further you will know when hand trading started, and algorithmic trading took a year.
When did algorithmic trading start?
Going back in time, the conventional trading practice began four centuries ago, which was around 1602 when the Dutch East India Company initiated the trading practice. And, it was not until the late 1980s and 1990s that Algorithmic trading (fully electronic execution of trade) began in financial markets.
In 1998, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) allowed e-commerce to pave the way for High-Frequency Trading (HFT) trading. And as HFT was able to trade 1000 times more than man, it increased dramatically.
High-Frequency Trading (HFT) is a form of automated trading, a definition we will see in the future.
Although Algorithmic trading is a single concept of trading, there are different wavelengths (speed) in which the stock market operates.
Frequencies of trading: HFT, MFT, LFT
Now, there is a certain level of speed at which trading (buying and selling stocks) takes place. This speed determines the amount of profit generated per second.
Below, let’s look at three common types of trading, each according to its frequency or speed.
High-Frequency Trading (HFT) – This type of trading leads to high-speed trading, i.e., large numbers of orders are made in seconds. Therefore, it makes safe trading possible in the market every millisecond, which makes it very profitable. This type of trading is a low trading practice which means that trading takes place much faster than the competition that responds to market events to increase profits.
An Insightful takeaway
- Higher trading is gaining popularity due to exchanges that provide incentives for firms/companies to add to market value.
- It helps to increase revenue in the market and also to eliminate small bid-ask spreads.
- In India, HFT accounts for one-third of its financial sector and is growing rapidly, making it the fastest-growing country in the world.
Medium-Frequency Trading (MFT) – Medium Frequency Trading takes a few minutes to a day to set up trading, therefore, it is slower than most common trades. Its delay (the time taken to set up trading) is higher than HFT.
Low-Frequency Trading (LFT) – Low Frequent trading takes place in a day to a few weeks and is a slow-moving form of trading. Therefore, the latency time (time taken to make a trade) is much higher than HFT and MFT.
In the US and other developed countries, High-Frequency Trading accounted for about 70% of revenue in 2013.
Hold on a minute! We have not yet reached the end. Since algorithmic trading requires highly profitable decision-making strategies, there are various strategies, each based on different market conditions.
Algorithmic Trading Strategies
Algorithm trading strategies are a variety of ideas to make algorithmic trading more profitable. Although each strategy is different, it remains the same as the process of conducting Algo trading. Each method is structured in such a way that it begins with the acquisition of real market data feeds from exchanges with predefined rules or terms, builds trade. A trade order contains all the details such as type, size, and quantity.
Each strategy works in its own pre-defined way to give the trader accurate execution of trading algorithms.
For a better understanding, see the list of most popular strategies and their meanings:
- Market-Making Strategies
- Arbitrage Strategies
- Statistical Strategies
- Momentum Strategies
- Sentiment Based Trading Strategies
- Machine Learning Trading Strategies
Market-Making Strategies:
This strategy helps to increase the liquidity in the markets. The market maker, usually a large center, makes it easy to order large buy and sell orders. The reason why market makers are great institutions is that there is a lot of security involved in the same thing. Therefore, it may not be possible for each connector to simplify the type of volume required.
In this process, market makers buy and sell security for a particular set of firms. Every market maker works by displaying buy and sell quotes for a specific security number. As soon as the order is received from the buyer, the market maker sells the shares in their list and completes the order. Therefore, it ensures monetization in the financial markets that make it easier for investors and traders to buy and sell. This sums up the fact that market makers are very important to adequate trading.
Arbitrage Strategies:
This strategy implies taking advantage of the mispricing of the financial instrument or asset in two different markets. An example of Arbitrage Strategies is an asset that trades in the market at a certain price but also trades at a much higher price in another market. Therefore, if you bought the property at a lower cost before, you could sell the same at the market where it was priced higher. This way, you will end up making a profit without taking any risk.
Therefore, this is a situation where you make multiple trades simultaneously on a single asset without a risk involved due to price inequality.
Statistical Arbitrage Strategies:
Based on the mean reversion hypothesis, statistical arbitrage algorithms work mostly as a pair. such strategies expect to benefit from the statistical estimate of one or more assets on the basis of the expected value of the asset.
One example of Statistical Arbitrage is trading in pairs where we look at the rate or spread between stocks, combined. If the spread rate exceeds the expected range, then you buy a declining stock and sell the previous stock in anticipation that the spread will return to its normal level. Statistical arbitrage can operate with a hundred or more shares in its portfolio that are categorized and can be fully automated in both analytics and performance.
Momentum Strategies:
These strategies profit from the market swings by looking at the existing trend in the market. So it wants to buy more and sell more by making investments in stocks profitable.
Now, let’s learn about the relationship between Value investment and Momentum investment.
When it comes to investing in stocks, it wants to get back to its value or mid-term whenever it deviates from it. This happens when the Momentum investment happens because it happens in space at a time before the emergence of a mean setback. Momentum works because of the large number of emotional decisions some traders make in the market at a time when prices are far from clear. Thus, profit is the result of bias and misconduct.
The only deceptive part here is that styles can quickly change and disrupt the gain of momentum, making these strategies very flexible. It is therefore very important to plan the purchase and sale properly and prevent losses. This can be done with appropriate risk management strategies that can effectively monitor investments and take precautionary measures in the face of adverse inflation.
We talked about dynamic trading strategies in our article about Algorithmic Trading strategies & Paradigms.
Sentiment Based Trading Strategies:
A sentiment trading strategy involves taking a position in a bull-or-bear market. The strategy of trading the emotions can be based on the momentum which means going with the consensus or the market and if it is capital we invest more and sell more or vice versa.
A sentiment trading strategy may work or go backward which means the opposite of market sentiment. The benefit is derived from the assumption that when there is a certain behavior of the crowd in terms of security, it increases certain consumer prices (exacerbating existing security increases) and that the capital is followed by a decrease in security prices due to repairs or vice versa.
Machine Learning Trading Strategies
Machine learning means studying algorithms and a specific set of patterns followed by computer programs to make trading decisions based on market data. A “pattern recognition” study, emphasizes the fact that computers learn without direct programming. It should now be clarified that people are building / launching software and then, in AI (Artificial Intelligence) it is developing itself for some time. It, therefore, means that human intervention is always needed. The advantage here is that machine-based models analyze a large amount of data at high speed and perform self-improvement. This is much simpler than the standard basic computer system developed by data scientists.
This was about different strategies in which algorithms could be developed and traded.
What are the rules and regulations in India?
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), the governing body, has issued specific regulations and compliance to ensure transparency and security of trade. The Forward Market Commission (FMC), a former commodity market manager, merged with SEBI in December 2015. It listed some of the most important requirements for algorithmic trading alignment in Indian markets.
You can read them below:
Audit Requirements – All HFT firms that require an annual audit can only be done by Exchange Impaneled system (CISA Certified) exchanges listed on the exchange website. According to the need for audit, you need to keep order logs, trading, control parameters, etc. A few years ago. Now you should know that regulatory parameters are especially needed for Indian trading to understand whether a set order strategy is validated or not.
Execution Related – Here is some correlation with respect to ordering. First, it concludes that all orders must be marked with a different identifier as defined by the rotation. Second, new orders can only be made after calculating the previously unknown order. Any changes to the algorithms should be allowed in rotation and the system should have enough checks to complete the execution in the event of a loop or run.
Commodity Markets specific – There are certain risk management measures such as Daily Price Range, Maximum Order Size, Stop Limit, etc. Things to follow. Additionally, Market and IOC orders (Immediate or cancel) orders will not be placed, only Limit orders may be placed. Small and medium-sized contracts do not enjoy Algorithmic trading. Also, all orders must be delivered via member servers located in India and approved IDs. These applications cannot contain links to any program or ID available / connected outside of India. Members must ensure that their strategy generates revenue in the market and must submit a document stating the same. Members will also keep all logs as described above and ensure regular auditing and approval of any changes to existing strategies.
All right! Now that you are clear about the many important tangents of Algorithmic Trading, let’s move on and explore a few more!
How to learn algorithmic trading?
Depending on the number of courses available online in Algorithmic trading, there are several that are shown, but finding the right one for your needs is very important. Now, it is clear that your interest is to learn from a team of market experts. To make this happen, you need to make sure your goal is set and look for information on the same basis. In short, your goal and the course you are giving should be in perfect harmony so as not to waste even an iota of time on unnecessary information.
In addition, there is a well-designed platform to use your knowledge, so you can use the same appropriately in the live market. Some of them are listed here.
Recommended Read:
Learn Algorithmic Trading: A Step By Step Guide
Books
There are several books on Algorithmic trading, which are important in understanding details such as, “how trading/exchange takes place in the market” and further research on market participants, trading methods, fluids, price availability, transaction costs, etc.
Read the blog, Essential Books on Algorithmic Trading, for a detailed synopsis of each of the relevant reads mentioned below:
- Trading and Exchanges: Market Microstructure for Practitioners by Larry Harris
- Market Microstructure Theory by Maureen O’Hara
- Algorithmic Trading: Winning Strategies and Their Rationale by Dr. Ernest Chan
- Algorithmic Trading and DMA: An introduction to direct access trading strategies by Barry Johnson
- Schaum’s Outline of Statistics and Econometrics by Dominick Salvatore, Derrick Reagle
- Analysis of Financial Time Series by Ruey Tsay
- Technical Analysis of the Financial Markets: A Comprehensive Guide to Trading Methods and Applications by John J. Murphy
- Options, Futures, and Other Derivatives by John C. Hull
- Dynamic Hedging: Managing Vanilla and Exotic Options by Nassim Nicholas Taleb
The books mentioned above will definitely enhance your knowledge and expertise in the various fields of the algorithmic trading field.
The workflow of Algorithmic Trading
Coming to the “understanding of workflow”, is a concept that describes how each trade is positioned using algorithms behind the scenes. Simply put, an algorithmic system works by obtaining data from an exchange on the basis on which a trade is placed.
Historically, Manual trading was rampant, in which, a trader was required to collect data by hand and place an order by telephone in order to trade. That would require a lot of time and effort and therefore, not make much profit because there was not much trading going on
Now with the advent of Algorithmic trading, the whole process of collecting market data until a trade order is placed is automatic.
When it comes to the way a multi-factor analyst moves while using algorithmic trading, here is a simplified diagram:
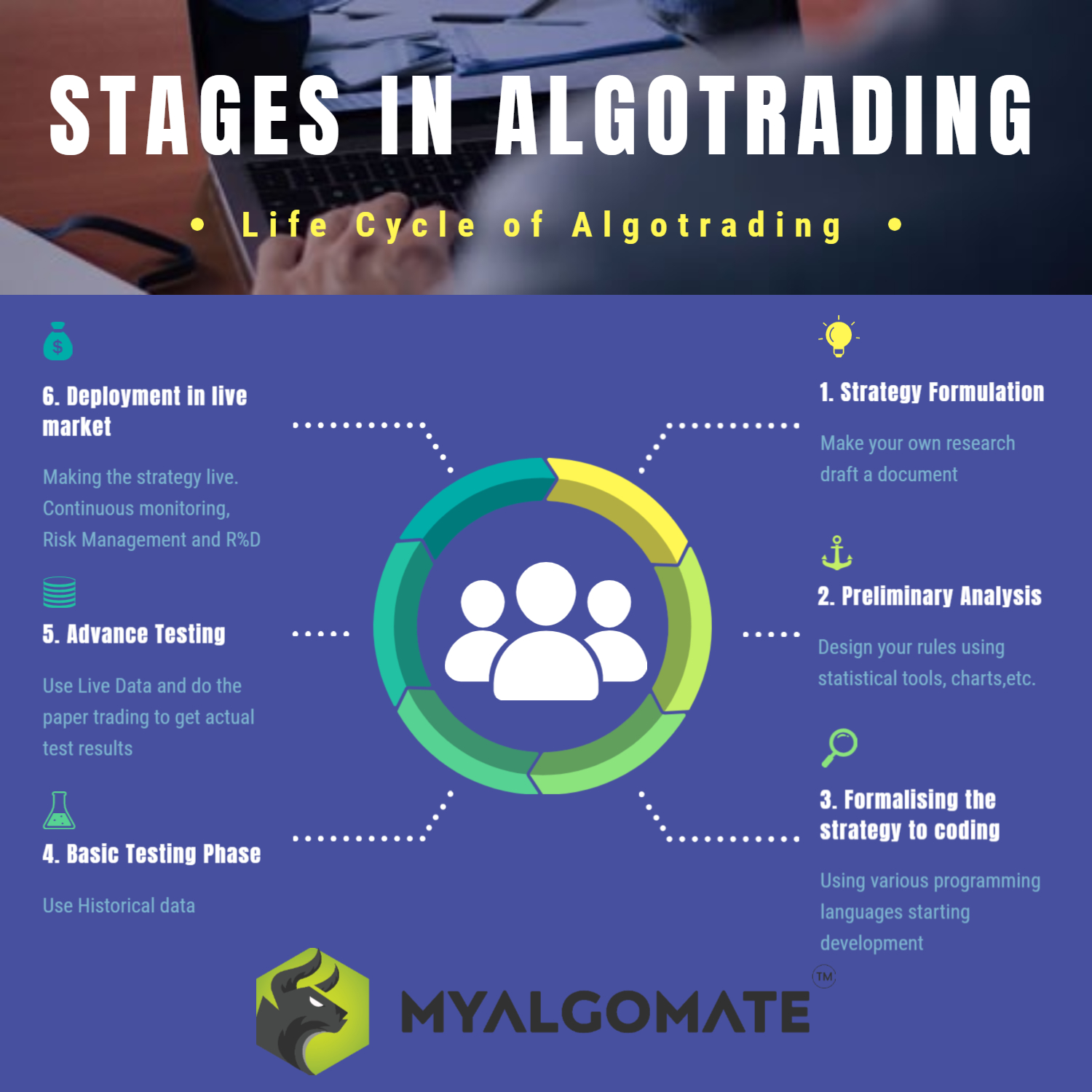
Therefore, the diagram above shows how value applies algorithmic trading.
In the first step, you will need to do some research or find some information that leads to the idea. That way your strategy will be based on the hypothesis you have set.
Then, in the second step, with the help of initial analysis and the use of mathematical tools, the rules are designed to trade.
In the third step, the strategy is officially implemented in coded language using one of the programming languages. This is done for a trading/computer trading platform to understand the strategy in languages that are understood in it.
Now, in the fourth step, test phase 1 is done with Backtesting, where historical data values are considered. In this case, the strategy is tested using historical data to understand how well logic would work if you used this in the past. In this way, the effectiveness of the strategy is tested. Also, depending on the results you get the opportunity to expand the strategy and its parameters.
After that, the fifth step is Phase 2 Test where the strategy test takes place in the real world. In this case, you do not need to invest real money but it still, gives you the most accurate and direct result. So, with this, one can expect to get results that can also occur in nature itself. The only thing that comes back is that it is a time-consuming job but you can do this using the feature provided by his vendor. Alternatively, you can also improve your game testing framework.
The sixth step involves Deployment in the real environment, which requires multiple frameworks to be managed, which is rarely considered in retrospective testing.
Functionally, the following aspects are required to be managed:
- Order management
- Risk Management
- Money/Fund Management
- Diversification of assets
- Portfolio management
- User Management
- Slippages
Technically, the following things need to be managed:
- Establish a connection with the broker API.
- Transfer buy/sell orders using the broker connection
- Establish a link to the API for data (if the data vendor is different from the broker)
- Access real-time and historical data using API data connections
Conclusion
Lastly, the algorithmic trading business is sure to provide you with an advanced trading and profit-making system and has become a popular method of trading.
Therefore, with the right information, common compliance, and regulations, the algorithmic trading platform is very fast, secure, and highly profitable.
Disclaimer: All data and information provided in this article are for informational purposes only. Myalgomate™ makes no representations as to accuracy, completeness, correctness, suitability, or validity of any information in this article and will not be liable for any errors, omissions, or delays in this information or any losses, injuries, or damages arising from its display or use. All information is provided on an as-is basis.


9 Comments
Best Copy Trading Software - Ranked #1 - India - Myalgomate
January 22, 2025[…] Check out our other blogs on Algo Trading: Copy Trading, What is Algorithmic Trading? […]
Algo Trading Vs Manual Trading: Which Method Is Right For You? - Myalgomate
April 8, 2023[…] out our other blogs on Algo Trading: Top 10 Intraday Trading Principles, What is Algorithmic Trading? , Things to Know Before Starting Algorithmic Trading and Learn Algorithmic Trading: A Step By […]
Boost Your Algo Trading With Co-location Server - Myalgomate
March 24, 2023[…] out our other blogs on Algo Trading: Top 10 Intraday Trading Principles, What is Algorithmic Trading? , Things to Know Before Starting Algorithmic Trading and Learn Algorithmic Trading: A Step By […]
Top 10 Rules For Successful Trading - Myalgomate
June 25, 2022[…] out our other blogs on Algo Trading: Top 10 Intraday Trading Principles, What is Algorithmic Trading? , Things to Know Before Starting Algorithmic Trading and Learn Algorithmic Trading: A Step By […]
Top 10 Intraday Trading Principles for Beginners - Myalgomate
April 16, 2022[…] out our other blogs on Algo Trading: What is Algorithmic Trading? , Things to Know Before Starting Algorithmic Trading and Learn Algorithmic Trading: A Step By […]
Freak Trade in NSE, All you need to know before its too late! - Myalgomate
September 10, 2021[…] placing continuous orders because of errors in the system using Algo Trading […]
Learn Algorithmic Trading: A Step By Step Guide - Myalgomate
August 18, 2021[…] beginners who want to venture into algorithmic trading, this article will serve as a guide to all the things that are essential to get you trading the […]
Algorithmic Trading Strategies, Paradigms And Modelling Ideas - Myalgomate
August 17, 2021[…] This concept is called Algorithmic Trading. […]
An Algorithmic Trading Guide For Retail Traders - Myalgomate
July 24, 2021[…] To read in detail about Algorithmic trading, you can refer to the article here. […]